Page 15 - 4498
P. 15
1.7. Consequences from the Main Equation of Molecular-Kinetic
Theory of Ideal Gas. Ideal Gas Laws.
The before established experimental gas laws follow from the main
equation of molecular-kinetic theory of ideal gas.
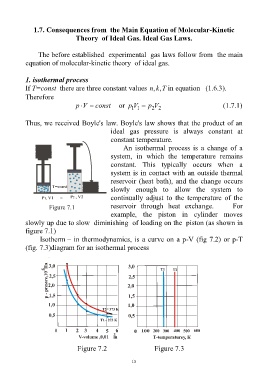
1. isothermal process
If T=const there are three constant values kn ,, T in equation (1.6.3).
Therefore
p V const or Vp 1 1 p 2 V (1.7.1)
2
Thus, we received Boyle's law. Boyle's law shows that the product of an
ideal gas pressure is always constant at
constant temperature.
An isothermal process is a change of a
system, in which the temperature remains
constant. This typically occurs when a
system is in contact with an outside thermal
reservoir (heat bath), and the change occurs
slowly enough to allow the system to
continually adjust to the temperature of the
Figure 7.1 reservoir through heat exchange. For
example, the piston in cylinder moves
slowly up due to slow diminishing of loading on the piston (as shown in
figure 7.1)
Isotherm – in thermodynamics, is a curve on a p-V (fig 7.2) or p-T
(fig. 7.3)diagram for an isothermal process
Figure 7.2 Figure 7.3
15