Page 46 - 4660
P. 46
Continuous random variables
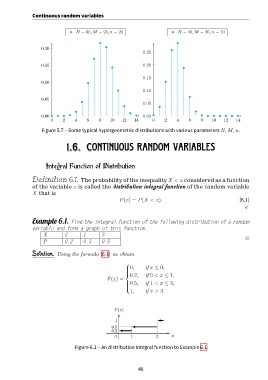
N = 60, M = 25, n = 20 N = 40, M = 15, n = 10
0.20
0.25
0.15 0.20
0.15
0.10
0.10
0.05
0.05
0.00 0.00
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
Figure 5.7 – Some typical hypergeometric distributions with various parameters N, M, n.
1.6. Continuous random variables
Integral Function of Distribution
Definition 6.1. The probability of the inequality X < x considered as a function
of the variable x is called the distribution integral function of the random variable
X that is
F(x) = P(X < x). (6.1)
✓
Example 6.1. Find the integral function of the following distribution of a random
variable and form a graph of this function.
X 0 1 3
,
P 0.2 0.3 0.5
Solution. Using the formula (6.1) we obtain
0, if x ≤ 0,
0.2, if 0 < x ≤ 1,
F(x) =
0.5, if 1 < x ≤ 3,
1, if x > 3.
F(x)
1
0.5
0.2
0 1 3 x
Figure 6.1 – An distribution integral function to Example 6.1
46