Page 25 - 4498
P. 25
1.13 Diffusion
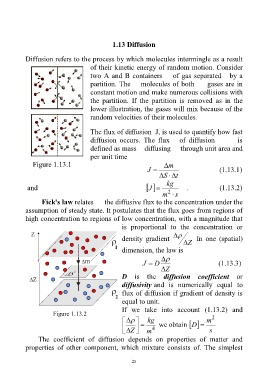
Diffusion refers to the process by which molecules intermingle as a result
of their kinetic energy of random motion. Consider
two A and B containers of gas separated by a
partition. The molecules of both gases are in
constant motion and make numerous collisions with
the partition. If the partition is removed as in the
lower illustration, the gases will mix because of the
random velocities of their molecules.
The flux of diffusion J, is used to quantify how fast
diffusion occurs. The flux of diffusion is
defined as mass diffusing through unit area and
per unit time
Figure 1.13.1 m
J (1.13.1)
S t
kg
and J . (1.13.2)
m 2 s
Fick's law relates the diffusive flux to the concentration under the
assumption of steady state. It postulates that the flux goes from regions of
high concentration to regions of low concentration, with a magnitude that
is proportional to the concentration or
density gradient In one (spatial)
Z
dimension, the law is
J D (1.13.3)
Z
D is the diffusion coefficient or
diffusivity and is numerically equal to
flux of diffusion if gradient of density is
equal to unit.
If we take into account (1.13.2) and
Figure 1.13.2
kg m 2
D
4 we obtain
Z m s
The coefficient of diffusion depends on properties of matter and
properties of other component, which mixture consists of. The simplest
25