Page 53 - 4560
P. 53
can keep straight shape, but may lose it due to even slight
influence.
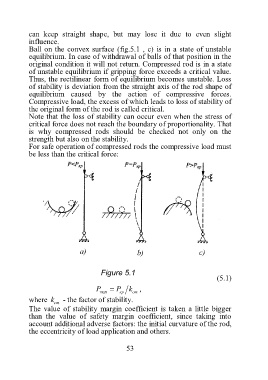
Ball on the convex surface (fig.5.1 , c) is in a state of unstable
equilibrium. In case of withdrawal of balls of that position in the
original condition it will not return. Compressed rod is in a state
of unstable equilibrium if gripping force exceeds a critical value.
Thus, the rectilinear form of equilibrium becomes unstable. Loss
of stability is deviation from the straight axis of the rod shape of
equilibrium caused by the action of compressive forces.
Compressive load, the excess of which leads to loss of stability of
the original form of the rod is called critical.
Note that the loss of stability can occur even when the stress of
critical force does not reach the boundary of proportionality. That
is why compressed rods should be checked not only on the
strength but also on the stability.
For safe operation of compressed rods the compressive load must
be less than the critical force:
Figure 5.1
(5.1)
P P k ,
max кр ст
where k - the factor of stability.
ст
The value of stability margin coefficient is taken a little bigger
than the value of safety margin coefficient, since taking into
account additional adverse factors: the initial curvature of the rod,
the eccentricity of load application and others.
53