Page 34 - 4560
P. 34
3.2 The force method. The canonical equation
The force method - is the most common method of disclosure of
statistical indetermination of rods, beams, and rod systems
(frames, arches, trusses, etc.).
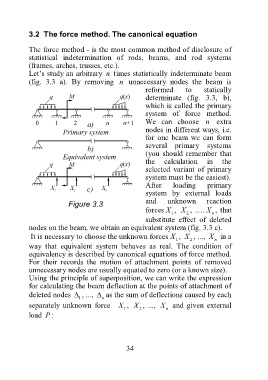
Let’s study an arbitrary n times statistically indeterminate beam
(fig. 3.3 a). By removing n unnecessary nodes the beam is
reformed to statically
determinate (fig. 3.3, b),
which is called the primary
system of force method.
We can choose n extra
nodes in different ways, i.e.
for one beam we can form
several primary systems
(you should remember that
the calculation in the
selected variant of primary
system must be the easiest).
After loading primary
system by external loads
and unknown reaction
Figure 3.3
forces X , X , …. X , that
1 2 n
substitute effect of deleted
nodes on the beam, we obtain an equivalent system (fig. 3.3 c).
It is necessary to choose the unknown forces X , X , ..., X in a
1 2 n
way that equivalent system behaves as real. The condition of
equivalency is described by canonical equations of force method.
For their records the motion of attachment points of removed
unnecessary nodes are usually equated to zero (or a known size).
Using the principle of superposition, we can write the expression
for calculating the beam deflection at the points of attachment of
deleted nodes , ..., as the sum of deflections caused by each
1 n
separately unknown force X , X , ..., X and given external
1 2 n
load P :
34