Page 69 - 4498
P. 69
L = T (S – S ) – (J – J ) (3.4.1)
L
G
L
min
G
0
where T is the temperature of the surroundings, S and S are,
0
L
G
respectively, the entropies of the gas and liquid, and J and J are the heat
L
G
content (enthalpies) of the gas and
liquid.
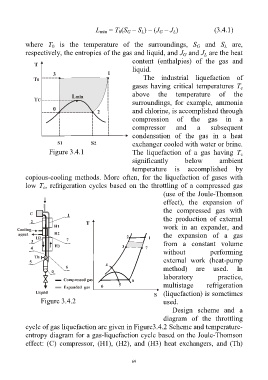
The industrial liquefaction of
gases having critical temperatures T
c
above the temperature of the
surroundings, for example, ammonia
and chlorine, is accomplished through
compression of the gas in a
compressor and a subsequent
condensation of the gas in a heat
exchanger cooled with water or brine.
Figure 3.4.1 The liquefaction of a gas having T
c
significantly below ambient
temperature is accomplished by
copious-cooling methods. More often, for the liquefaction of gases with
low T , refrigeration cycles based on the throttling of a compressed gas
c
(use of the Joule-Thomson
effect), the expansion of
the compressed gas with
the production of external
work in an expander, and
the expansion of a gas
from a constant volume
without performing
external work (heat-pump
method) are used. In
laboratory practice,
multistage refrigeration
(liquefaction) is sometimes
Figure 3.4.2 used.
Design scheme and a
diagram of the throttling
cycle of gas liquefaction are given in Figure3.4.2 Scheme and temperature-
entropy diagram for a gas-liquefaction cycle based on the Joule-Thomson
effect: (C) compressor, (H1), (H2), and (H3) heat exchangers, and (Th)
69