Page 72 - 4498
P. 72
3.5. Liquids. Surface Tension
Liquids are substances that are incompressible but offering now resistance
to change the shape and are assumed to have the shape of vessels in which
they are. Liquids have the specific type of molecular heat motion. A
molecule in a liquid for some time oscillates around certain equilibrium
position but after some time a molecule displaces at a new equilibrium
position. Simultaneous slow displacements of molecules and their vibrations
within small volumes take place.
The molecules of liquid move under the influence of strong forces exerted
by the nearest neighbors. These forces are repulsive when the molecules
approach too closely and attractive when the leparation is greater than
normal. For a molecule within the liquid the time average of these internal
forces is zero. However, if I molecule at a surface begins to leave the
liquid, the resultant of these forces pulls it back. A molecule must have
considerable energy to escape the surface.
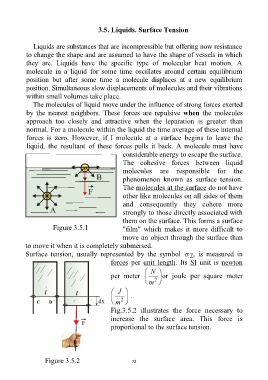
The cohesive forces between liquid
molecules are responsible for the
phenomenon known as surface tension.
The molecules at the surface do not have
other like molecules on all sides of them
and consequently they cohere more
strongly to those directly associated with
them on the surface. This forms a surface
Figure 3.5.1 "film" which makes it more difficult to
move an object through the surface than
to move it when it is completely submersed.
Surface tension, usually represented by the symbol γ, is measured in
forces per unit length. Its SI unit is newton
N
per meter or joule per square meter
m 2
J
2 .
С D m
Fig.3.5.2 illustrates the force necessary to
increase the surface area. This force is
proportional to the surface tension.
Figure 3.5.2 72