Page 15 - 4911
P. 15
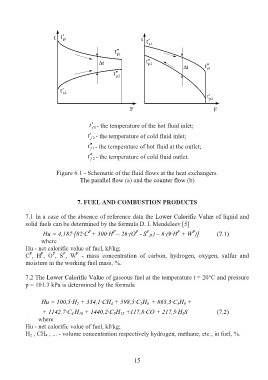
t t 1 p t
t
1 p
t
1 p
t t p 2
t t 1 p
t
p 2
t
p 2
t
p 2
F F
t 1 f - the temperature of the hot fluid inlet;
t f 2 - the temperature of cold fluid inlet;
t 1 f - the temperature of hot fluid at the outlet;
t f 2 - the temperature of cold fluid outlet.
Figure 6.1 - Schematic of the fluid flows at the heat exchangers.
The parallel flow (a) and the counter flow (b)
7. FUEL AND COMBUSTION PRODUCTS
7.1 In a case of the absence of reference data the Lower Calorific Value of liquid and
solid fuels can be determined by the formula D. I. Mendeleev [5]
P
P
P
P
P
P
Hu = 4,187·[82·C + 300·H – 26·(O - S Л ) – 6·(9·H + W )] (7.1)
where
Hu - net calorific value of fuel, kJ/kg;
P
P
P
P
P
C , H , O , S , W - mass concentration of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur and
moisture in the working fuel mass, %.
7.2 The Lower Calorific Value of gaseous fuel at the temperature t = 20°C and pressure
p = 101.3 kPa is determined by the formula
Hu = 100,5·H 2 + 334,1·CH 4 + 598,5·C 2H 6 + 865,3·C 3H 8 +
+ 1142,7·C 4 H 10 + 1440,2·C 5H 12 +117,8·CO + 217,5·H 2S (7.2)
where
Hu - net calorific value of fuel, kJ/kg;
H 2 , CH 4 , ... - volume concentration respectively hydrogen, methane, etc., in fuel, %.
15