Page 18 - 4749
P. 18
assumption is well confirmed by experiments (it is not limited to
small deformations in elastic materials). For example, the
establishment of a small clamp on a long thick-walled rubber tube
will cause significant deformation only near the load location.
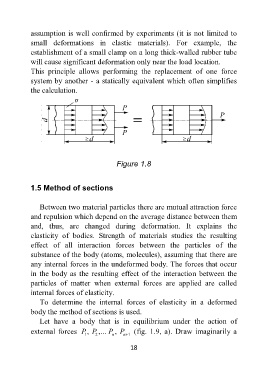
This principle allows performing the replacement of one force
system by another - a statically equivalent which often simplifies
the calculation.
Figure 1.8
1.5 Method of sections
Between two material particles there are mutual attraction force
and repulsion which depend on the average distance between them
and, thus, are changed during deformation. It explains the
elasticity of bodies. Strength of materials studies the resulting
effect of all interaction forces between the particles of the
substance of the body (atoms, molecules), assuming that there are
any internal forces in the undeformed body. The forces that occur
in the body as the resulting effect of the interaction between the
particles of matter when external forces are applied are called
internal forces of elasticity.
To determine the internal forces of elasticity in a deformed
body the method of sections is used.
Let have a body that is in equilibrium under the action of
external forces P , ,... , P P P (fig. 1.9, a). Draw imaginarily a
1 2 n n 1
18