Page 116 - 4624
P. 116
()
determined by taking the time derivative of the path function s = st
i.e., v = ds / dt . Hence
v = vu 2-31
t
where
s
v = ɺ
Acceleration. The acceleration of the particle is the time rate of
change of the velocity. Thus,
a = v ɺ = vu ɺ t + vu ɺ t 2-32
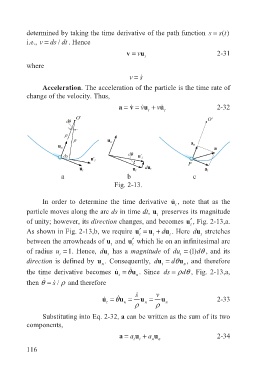
a b c
Fig. 2-13.
In order to determine the time derivative u ɺ , note that as the
t
particle moves along the arc ds in time dt, u preserves its magnitude
t
of unity; however, its direction changes, and becomes ′ u , Fig. 2-13,a.
t
As shown in Fig. 2-13,b, we require ′ =u t u t + du . Here du stretches
t
t
between the arrowheads of u and ′ u which lie on an infinitesimal arc
t
t
of radius u = 1. Hence, du has a magnitude of du = (1)dθ , and its
t
t
t
direction is defined by u . Consequently, du t = dθu , and therefore
n
n
ɺ
the time derivative becomes u ɺ t = θu . Since ds = ρθ
d , Fig. 2-13,a,
n
ɺ
then θ = ɺ / s ρ and therefore
ɺ
u ɺ = θu = s ɺ u = v u 2-33
n
t
ρ n ρ n
Substituting into Eq. 2-32, a can be written as the sum of its two
components,
a = a u t + a u 2-34
n
t
n
116