Page 39 - 4567
P. 39
drilled too far off-structure, it might not encounter commercial amounts of oil or gas and is
called a dry hole, duster, or wet well.
In a trap, the reservoir rock must be overlain by a caprock or seal, an impermeable rock
layer that does not allow fluids to flow through it. Without a caprock or seal, the gas and oil
would leak onto the surface.
Two common caprocks are shales and salt layers. Well-cemented or shaly rocks, very-
fine-grained limestone (micrite or chalk), and permafrost can also be caprocks.
A field is the surface area directly above one or more producing reservoirs on the same
trap, such as an anticline. Fields are commonly named after a geographic area such as a town,
hill, or creek. A reservoir is a subsurface zone that produces oil and gas but does not
communicate with other reservoirs. Fluids cannot flow from one reservoir to another. The oil or
gas in a single reservoir has the same characteristics throughout the reservoir but can be very
different between reservoirs in the same field. A pressure system that is common to several
adjacent reservoir rocks indicates a single reservoir.
Task 3. Copy out all the terms from the text, translate them and provide a glossary for
them.
Task 4. Answer the following questions, using the vocabulary from Task 1.
1. What does the generation of a crude oil or natural gas from a solid (organic matter) cause?
2. What is lighter in density: gas and oil or the water?
3. What are carrier beds?
4. What process is called migration?
5. Why is a trap important in the process of oil and gas migration?
6. What is the most common trap?
7. Does an unsaturated pool lack a free gas cap?
8. What is crest?
9. What happens if the first exploratory well is usually drilled on-structure? Off-structure?
10. What is a caprock or seal used for?
11. What are the two common caprocks?
12. What is bigger: a field or a reservoir?
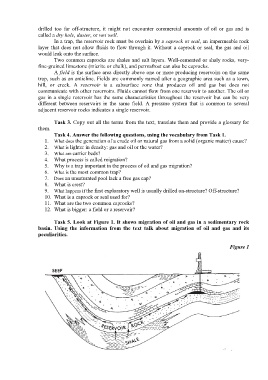
Task 5. Look at Figure 1. It shows migration of oil and gas in a sedimentary rock
basin. Using the information from the text talk about migration of oil and gas and its
peculiarities.
Figure 1