Page 81 - 4498
P. 81
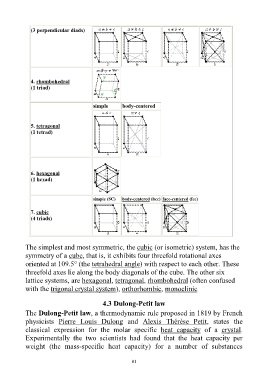
(3 perpendicular diads)
4. rhombohedral
(1 triad)
simple body-centered
5. tetragonal
(1 tetrad)
6. hexagonal
(1 hexad)
simple (SC) body-centered (bcc) face-centered (fcc)
7. cubic
(4 triads)
The simplest and most symmetric, the cubic (or isometric) system, has the
symmetry of a cube, that is, it exhibits four threefold rotational axes
oriented at 109.5° (the tetrahedral angle) with respect to each other. These
threefold axes lie along the body diagonals of the cube. The other six
lattice systems, are hexagonal, tetragonal, rhombohedral (often confused
with the trigonal crystal system), orthorhombic, monoclinic
4.3 Dulong-Petit law
The Dulong-Petit law, a thermodynamic rule proposed in 1819 by French
physicists Pierre Louis Dulong and Alexis Thérèse Petit, states the
classical expression for the molar specific heat capacity of a crystal.
Experimentally the two scientists had found that the heat capacity per
weight (the mass-specific heat capacity) for a number of substances
81