Page 83 - 4498
P. 83
In the very low (cryogenic) temperature region, where the
quantum mechanical nature of energy storage in all solids
manifests itself with larger and larger effect, the law fails for all
substances. In 1912 Debye realized that, inconsistent with the Einstein
model, low-energetic excitations of a solid material were not oscillations
of a single atom, but collective modes propagating through the material.
Such vibrations can be considered to be sound waves, and their
propagation speed is the speed of sound in the material. Moreover, these
modes only accept energy in discreet amounts.
Quantum theory uses the concepts of phonons, which are “quasi-particles”
with definite energies and directions of motion, to treat the vibrations. The
concept of phonon is analogous with photons of the electromagnetic wave.
4.4 Crystallographic Defect
Crystalline solids exhibit a periodic crystal structure. The positions of
atoms or molecules occur on repeating fixed distances, determined by the
unit cell parameters. However, the arrangement of atoms or molecules in
most crystalline materials is not perfect. The regular patterns are
interrupted by crystallographic defects.
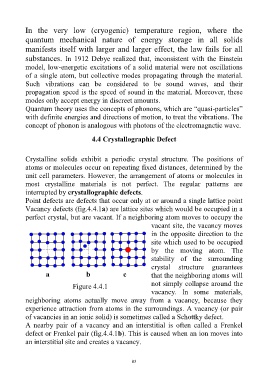
Point defects are defects that occur only at or around a single lattice point
Vacancy defects (fig.4.4.1a) are lattice sites which would be occupied in a
perfect crystal, but are vacant. If a neighboring atom moves to occupy the
vacant site, the vacancy moves
in the opposite direction to the
site which used to be occupied
by the moving atom. The
stability of the surrounding
crystal structure guarantees
a b c that the neighboring atoms will
not simply collapse around the
Figure 4.4.1
vacancy. In some materials,
neighboring atoms actually move away from a vacancy, because they
experience attraction from atoms in the surroundings. A vacancy (or pair
of vacancies in an ionic solid) is sometimes called a Schottky defect.
A nearby pair of a vacancy and an interstitial is often called a Frenkel
defect or Frenkel pair (fig.4.4.1b). This is caused when an ion moves into
an interstitial site and creates a vacancy.
83