Page 60 - Microsoft Word - 4236
P. 60
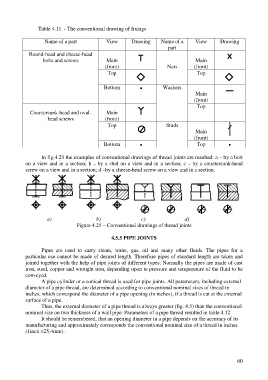
Table 4.11 - The conventional drawing of fixings
Name of a part View Drawing Name of a View Drawing
part
Round-head and cheese-head
bolts and screws Main Main
(front) Nuts (front)
Top Top
Bottom Washers
Main
(front)
Top
Countersunk-head and oval- Main
head screws (front)
Top Studs
Main
(front)
Bottom Top
In fig.4.25 the examples of conventional drawings of thread joints are resulted: a – by a bolt
on a view and in a section; b – by a stud on a view and in a section; c – by a countersunk-head
screw on a view and in a section; d –by a cheese-head screw on a view and in a section.
а) b) c) d)
Figure 4.25 – Conventional drawings of thread joints
4.5.5 PIPE JOINTS
Pipes are used to carry steam, water, gas, oil and many other fluids. The pipes for a
particular use cannot be made of desired length. Therefore pipes of standard length are taken and
joined together with the help of pipe joints of different types. Normally the pipes are made of cast
iron, steel, copper and wrought iron, depending upon te pressure and temperature of the fluid to be
conveyed.
A pipe cylinder or a conical thread is used for pipe joints. All parameters, including external
diameter of a pipe thread, are determined according to conventional nominal sizes of thread in
inches, which correspond the diameter of a pipe opening (in inches), if a thread is cut at the external
surface of a pipe.
Thus, the external diameter of a pipe thread is always greater (fig. 4.5) than the conventional
nominal size on two thickness of a wall pipe. Parameters of a pipe thread resulted in table 4.12.
It should be remembered, that an opening diameter in a pipe depends on the accuracy of its
manufacturing and approximately corresponds the conventional nominal size of a thread in inches
(1inch =25,4mm).
60