Page 51 - Microsoft Word - 4236
P. 51
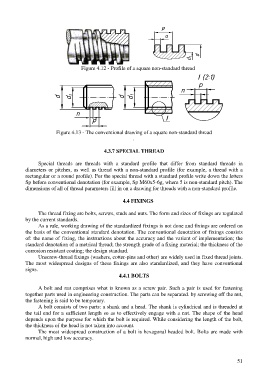
Figure 4.12 - Profile of a square non-standard thread
Figure 4.13 - The conventional drawing of a square non-standard thread
.
4.3.7 SPECIAL THREAD
Special threads are threads with a standard profile that differ from standard threads in
diameters or pitches, as well as thread with a non-standard profile (for example, a thread with a
rectangular or a round profile). For the special thread with a standard profile write down the letters
Sp before conventional denotation (for example, Sp M60x5-6g, where 5 is non-standard pitch). The
dimensions of all of thread parameters fill in on a drawing for threads with a non-standard profile.
4.4 FIXINGS
The thread fixing are bolts, screws, studs and nuts. The form and sizes of fixings are regulated
by the current standards.
As a rule, working drawing of the standardized fixings is not done and fixings are ordered on
the basis of the conventional standard denotation. The conventional denotation of fixings consists
of: the name of fixing, the instructions about the accuracy and the variant of implementation; the
standard denotation of a metrical thread; the strength grade of a fixing material; the thickness of the
corrosion resistant coating; the design standard.
Unscrew-thread fixings (washers, cotter-pins and other) are widely used in fixed thread joints.
The most widespread designs of these fixings are also standardized, and they have conventional
signs.
4.4.1 BOLTS
A bolt and nut comprises what is known as a screw pair. Such a pair is used for fastening
together parts used in engineering construction. The parts can be separated. by screwing off the nut,
the fastening is said to be temporary.
A bolt consists of two parts: a shank and a head. The shank is cylindrical and is threaded at
the tail end for a sufficient length so as to effectively engage with a nut. The shape of the head
depends upon the purpose for which the bolt is required. While considering the length of the bolt,
the thickness of the head is not taken into account.
The most widespread construction of a bolt is hexagonal headed bolt. Bolts are made with
normal, high and low accuracy.
51