Page 12 - 4234
P. 12
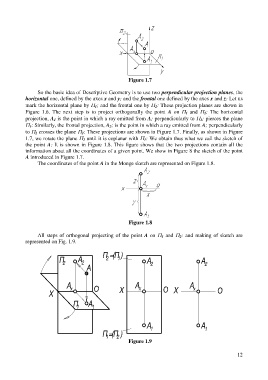
Figure 1.7
So the basic idea of Descriptive Geometry is to use two perpendicular projection planes, the
horizontal one, defined by the axes x and y; and the frontal one defined by the axes x and z: Let us
mark the horizontal plane by 1; and the frontal one by 2: These projection planes are shown in
Figure 1.6. The next step is to project orthogonally the point A on 1 and 2: The horizontal
projection, A 1 is the point in which a ray emitted from A; perpendicularly to 1; pierces the plane
1: Similarly, the frontal projection, A 2; is the point in which a ray emitted from A; perpendicularly
to 2 crosses the plane 2: These projections are shown in Figure 1.7. Finally, as shown in Figure
1.7, we rotate the plane 2 until it is coplanar with 1: We obtain thus what we call the sketch of
the point A: It is shown in Figure 1.8. This figure shows that the two projections contain all the
information about all the coordinates of a given point. We show in Figure 8 the sketch of the point
A introduced in Figure 1.7.
The coordinates of the point A in the Monge sketch are represented on Figure 1.8.
Figure 1.8
All steps of orthogonal projecting of the point A on 1 and 2: and making of sketch are
represented on Fig. 1.9.
П =(П)
П 2 A 2 2 1 A A
А 2 2
A О A x A
X x X О X x О
П 1 A 1
A 1 A 1
П=(П )
1
2
Figure 1.9
12