Page 8 - 342_
P. 8
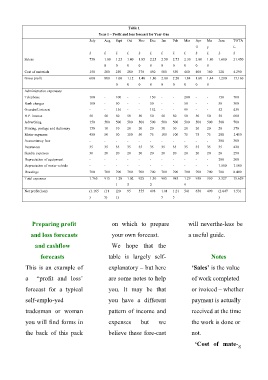
Table 1
Year 1 – Profit and loss forecast for Year One
July Aug Sept Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb Mar Apr Ma June TOTA
il y L
£ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £ £
Saless 750 1.00 1.25 1.40 1.85 2.25 2.50 2.75 2.30 2.00 1.80 1.600 21.450
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Cost of materials 150 200 250 280 370 450 500 550 460 400 360 320 4.290
Gross profit 600 800 1.00 1.12 1.48 1.80 2.00 2.20 1.84 1.60 1.44 1.280 17.160
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Administrative expensaes
Telephone 100 - 100 - - 150 - - 200 - - 150 700
Bank charges 100 - 50 - - 50 - - 50 - - 50 300
Overdraft interest - - 136 - - 152 - - 99 - - 52 439
H.P. interest 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 50 600
Advertising 150 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 500 700
Printing, postage and stationery 150 10 10 20 20 20 30 30 20 20 20 20 370
Motor expenses 450 50 50 150 50 75 100 100 75 75 75 200 1.450
Accountancy fees - - - - - - - - - - - 300 300
Insurances 35 35 35 35 35 35 35 35 35 35 35 35 420
Sundry expenses 30 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 250
Depreciation of equipment - - - - - - - - - - - 200 200
Depreciation of motor vehicle - - - - - - - - - - - 1.500 1.500
Drawings 700 700 700 700 700 700 700 700 700 700 700 700 8.400
Total expenses 1.765 915 1.20 1.02 925 1.30 985 985 1.29 950 950 3.327 15.629
1 5 2 9
Net profit (loss) (1.165 (11 (20 95 555 498 1.01 1.21 541 650 490 (2.047 1.531
) 5) 1) 5 5 )
Preparing profit on which to prepare will neverthe-less be
and loss forecasts your own forecast. a useful guide.
and cashflow We hope that the
forecasts table is largely self- Notes
This is an example of explanatory – but here ‘Sales’ is the value
a “profit and loss’ are some notes to help of work completed
forecast for a typical you. It may be that or ivoiced – whether
self-emplo-yed you have a different payment is actually
tradesman or woman pattern of income and received at the time
you will find forms in expenses but we the work is done or
the back of this pack believe these fore-cast not.
‘Cost of mate-
8