Page 29 - 4749
P. 29
N
x , (2.7)
o 1
br sin 2
2
where - the angle of the face side of the rod; - the angle
between the fiber and the axis of the rod; r - the radius of the
cylindrical surface of the rod.
At a low stress angle value obtained by the formula (2.5) is
close to the truth.
N N
x x .
A 2 b r tg
For example, if 12 , then the error does not exceed 2%.
2.4 Longitudinal and cross deformations
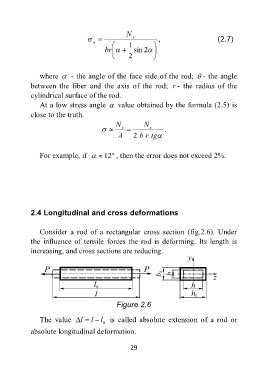
Consider a rod of a rectangular cross section (fig.2.6). Under
the influence of tensile forces the rod is deforming. Its length is
increasing, and cross sections are reducing.
Figure 2.6
The value l l l is called absolute extension of a rod or
0
absolute longitudinal deformation.
29