Page 115 - 4560
P. 115
Theorem 2. If the fluid pressure acts on an arbitrary surface, the
vertical component of force equal to the weight of fluid pressure
in the volume that is above the surface.
Stresses and are major. The third principal stress is
m t
perpendicular to the surface of the membrane and
is p (on the surface to which attached pressure). It is usually
much less than stresses and , we can neglect it and,
m t
assuming that the shell material is in plane stress. Terms of
strength, such as plastic material, take the form:
– third theory
or ; (9.7)
t m
– fourth theory
2
2
. (9.8)
t m t m
In calculating the tanks permissible stresses are installed in
accordance with accepted standards in Ukraine, taking into
account the brand of steel, structural peculiarities of tanks,
temperature control operation, aggressive environment and so on.
9.3 Lame’s problem
If the ratio of wall thickness to the inner radius of the cylinder
exceed 1/10, the cylinder should be regarded as thick-walled and
calculate it on the basis of a more accurate theory. This problem
was first solved by the French scientist G. Lame. When choosing
the theory for calculating it must be remembered that the
separation of cylinders for thick-walled and thin-walled is quite
conditional and linked to the required accuracy of calculation.
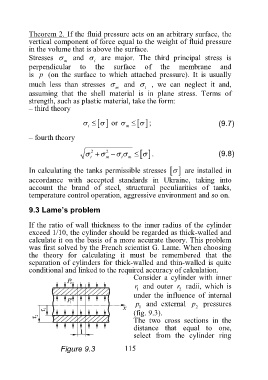
Consider a cylinder with inner
r and outer r radii, which is
1 2
under the influence of internal
p and external p pressures
1 2
(fig. 9.3).
The two cross sections in the
distance that equal to one,
select from the cylinder ring
Figure 9.3 115