Page 43 - 4498
P. 43
dp dV
0. (2.7.9)
p V
dp
So d ln p , then
p
ln pd lnV 0 d ln Vp 0 . (2.7.10)
Differential of constant magnitude is zero ,thus
p V const.
(2.7.11)
The derived equation (2.7.11) is called
adiabatic one or Poisson's equation (Siméon
Denis Poisson ( 1781 -1840), a French
mathematician, geometer, and physicist.) In
C
this equation special heat ratio P is
C V
called an adiabatic index.
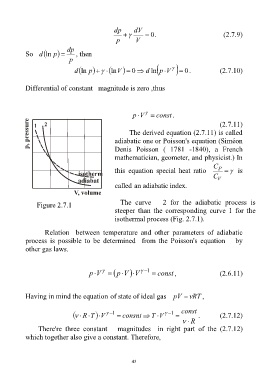
The curve 2 for the adiabatic process is
Figure 2.7.1
steeper than the corresponding curve 1 for the
isothermal process (Fig. 2.7.1).
Relation between temperature and other parameters of adiabatic
process is possible to be determined from the Poisson's equation by
other gas laws.
1
p V p V V const , (2.6.11)
Having in mind the equation of state of ideal gas pV RT ,
1 1 const
R T V consnt T V . (2.7.12)
R
There're three constant magnitudes in right part of the (2.7.12)
which together also give a constant. Therefore,
43