Page 41 - 4498
P. 41
V 2
m dV m V 2
A RT RT ln (2.6.10)
M V M V
V 1 1
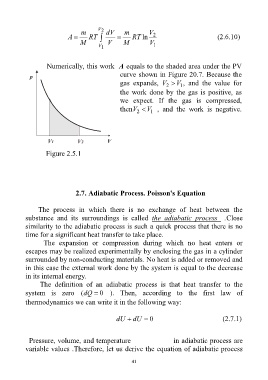
Numerically, this work A equals to the shaded area under the PV
curve shown in Figure 20.7. Because the
gas expands, V V , and the value for
1
2
the work done by the gas is positive, as
we expect. If the gas is compressed,
thenV V , and the work is negative.
2
1
Figure 2.5.1
2.7. Adiabatic Process. Poisson's Equation
The process in which there is no exchange of heat between the
substance and its surroundings is called the adiabatic process .Close
similarity to the adiabatic process is such a quick process that there is no
time for a significant heat transfer to take place.
The expansion or compression during which no heat enters or
escapes may be realized experimentally by enclosing the gas in a cylinder
surrounded by non-conducting materials. No heat is added or removed and
in this case the external work done by the system is equal to the decrease
in its internal energy.
The definition of an adiabatic process is that heat transfer to the
system is zero (dQ 0 ). Then, according to the first law of
thermodynamics we can write it in the following way:
dU dU 0 (2.7.1)
Pressure, volume, and temperature in adiabatic process are
variable values .Therefore, let us derive the equation of adiabatic process
41