Page 6 - 4461
P. 6
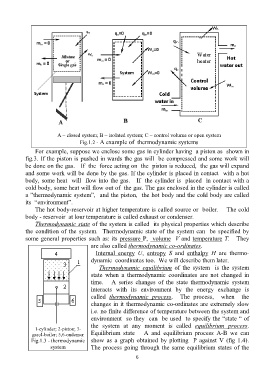
A – closed system; B – isolated system; C – control volume or open system
Fig.1.2 - A example of thermodynamic systems
For example, suppose we enclose some gas in cylinder having a piston as shown in
fig.3. If the piston is pushed in wards the gas will be compressed and some work will
be done on the gas. If the force acting on the piston is reduced, the gas will expand
and some work will be done by the gas. If the cylinder is placed in contact with a hot
body, some heat will flow into the gas. If the cylinder is placed in contact with a
cold body, some heat will flow out of the gas. The gas enclosed in the cylinder is called
a ”thermodynamic system”, and the piston, the hot body and the cold body are called
its “environment”.
The hot body-reservoir at higher temperature is called source or boiler. The cold
body - reservoir at lour temperature is called exhaust or condenser.
Thermodynamic state of the system is called its physical properties which describe
the condition of the system. Thermodynamic state of the system can be specified by
some general properties such as: its pressure P, volume V and temperature T. They
are also called thermodynamic co-ordinates.
Internal energy U, entropy S and enthalpy H are thermo-
dynamic coordinates too. We will describe them later.
Thermodynamic equilibrium of the system is the system
state when a thermodynamic coordinates are not changed in
time. A series changes of the state thermodynamic system
interacts with its environment by the energy exchange is
called thermodynamic process. The process, when the
changes in it thermodynamic co-ordinates are extremely slow
i.e. no finite difference of temperature between the system and
environment so they can be used to specify the “state “ of
the system at any moment is called equilibrium process.
1-cylinder; 2-piston; 3-
gas;4-boiler; 5,6-ondenser Equilibrium state A and equilibrium process A-B we can
Fig.1.3 - thermodynamic show as a graph obtained by plotting P against V (fig 1.4).
system The process going through the same equilibrium states of the
6