Page 39 - 4461
P. 39
material (gas) is very compressible. The compressor needs to handle a large volume and
achieve large compression ratios.
Analysis. The heat input in a gas turbine cycle is given by Q in = m cp (T 2 - T 1) and the
heat rejected Q out = m cp (T 3 - T 4). Thus the thermal efficiency is given by
T
4 1
Q T T T
1 out → 1 4 1 → 1 1 ( T 1 ) .
th th th T
Q T T T 3
in 3 2 2 1
T
2
Since the adiabatic processes take place between the same pressures, the temperature
ratios are the same
k 1 k 1
T P k k 1 T P k k 1
2 2 k ; 3 3 k ,
th th
T P T P
1 1 4 4
where β is the pressure ratio and k is the specific heat ratio. The pressure ratio is a
fundamental quantity for the gas-turbine cycle,
1
then th 1 k 1 (4.8)
k
Equation 4.8 shows that under the cold-air-standard assumptions, the thermal
efficiency of an ideal Brayton cycle depends on the pressure ratio of the gas turbine and
the specific heat ratio of the working fluid. The thermal efficiency increases with both
of these parameters, which is also the case for actual gas turbines.
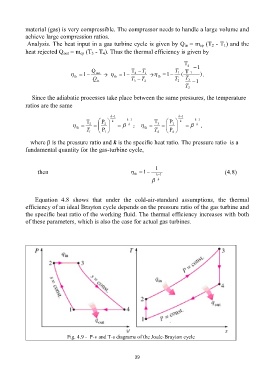
Fig. 4.9 - P-v and T-s diagrams of the Joule-Brayton cycle
39