Page 35 - 4461
P. 35
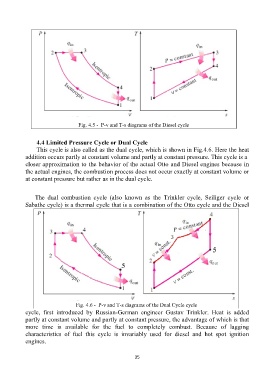
Fig. 4.5 - P-v and T-s diagrams of the Diesel cycle
4.4 Limited Pressure Cycle or Dual Cycle
This cycle is also called as the dual cycle, which is shown in Fig.4.6. Here the heat
addition occurs partly at constant volume and partly at constant pressure. This cycle is a
closer approximation to the behavior of the actual Otto and Diesel engines because in
the actual engines, the combustion process does not occur exactly at constant volume or
at constant pressure but rather as in the dual cycle.
The dual combustion cycle (also known as the Trinkler cycle, Seiliger cycle or
Sabathe cycle) is a thermal cycle that is a combination of the Otto cycle and the Diesel
Fig. 4.6 - P-v and T-s diagrams of the Dual Cycle cycle
cycle, first introduced by Russian-German engineer Gustav Trinkler. Heat is added
partly at constant volume and partly at constant pressure, the advantage of which is that
more time is available for the fuel to completely combust. Because of lagging
characteristics of fuel this cycle is invariably used for diesel and hot spot ignition
engines.
35