Page 21 - Microsoft Word - 4236
P. 21
Thus, to get a sectional drawing, it is necessary:
To make a cutting plane in the right place;
To set aside the part of an object, placed between the observer and the cutting plane;
To project the remaining, part on the proper plane of projections and depict on the place
of one of the basic views or on the free field of the drawing;
To design a sectional drawing, if it is necessary, with inscript.
It should be remembered that a sectional viewsis a conventional representation and the part of
an object, placed between an observer and a cutting plane, is set aside too. A conventional cutting
touches only this depiction and does not influence all the others. So, for example, a sectional views
on the frontal plane of projections does not change a top view.
Classification of sectional views.
The sectional views are divided according to the followings features:
1. Accoding to the position of a cutting plane in relation to the horizontal plane of projections
sectional views are divided into horizontal, vertical and inclined.
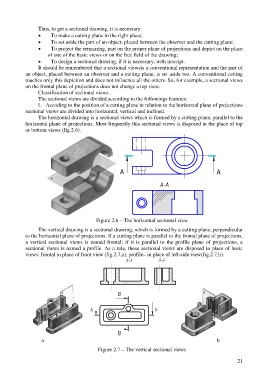
The horizontal drawing is a sectional views which is formed by a cutting plane, parallel to the
horizontal plane of projections. Most frequently this sectional views is disposed in the place of top
or bottom views (fig.2.6).
A A
А-А
Figure 2.6 – The horizontal sectional view
The vertical drawing is a sectional drawing, which is formed by a cutting plane, perpendicular
to the horizontal plane of projections. If a cutting plane is parallel to the frontal plane of projections,
a vertical sectional views is named frontal; if it is parallel to the profile plane of projections, a
sectional views is named a profile. As a rule, these sectional views are disposed in place of basic
views: frontal in place of front view (fig.2.7,a), profile– in place of left-side view(fig.2.7,b).
a b
Figure 2.7 – The vertical sectional views
21