Page 77 - 4234
P. 77
These are mapped orthographically to the plane parallel to the axis as line segments (Fig. 7.26).
Figure 7.26
Intersection of sphere and conical or cylindrical surface, which is not the surface of revolution,
can be determined as a set of intersection points of lines on the concerned surface with the sphere
by means of the system of auxiliary planes.
7.5.3 CUTTING-SPHERE METHOD
Cutting-sphere method divides into concentric cutting-sphere method and eccentric cutting-
sphere method.
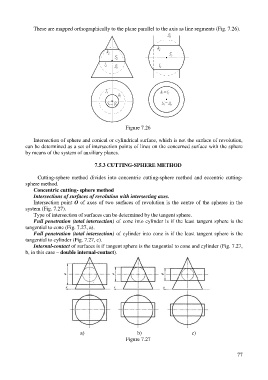
Сoncentric cutting- sphere method
Intersections of surfaces of revolution with intersecting axes.
Intersection point O of axes of two surfaces of revolution is the centre of the spheres in the
system (Fig. 7.27).
Type of intersection of surfaces can be determined by the tangent sphere.
Full penetration (total intersection) of cone into cylinder is if the least tangent sphere is the
tangential to cone (Fig. 7.27, a).
Full penetration (total intersection) of cylinder into cone is if the least tangent sphere is the
tangential to cylinder (Fig. 7.27, c).
Internal-contact of surfaces is if tangent sphere is the tangential to cone and cylinder (Fig. 7.27,
b, in this case – double internal-contact).
a) b) c)
Figure 7.27
77