Page 15 - 4167
P. 15
According to the definition of displacement quotient obtained
by dividing the vector of displacement by time t is vector l and this
vector is called velocity
r
v . (1.10)
t
Average velocity v of point's motion in time interval ∆t is the vector
namely quotient obtained by dividing the vector of displacement by
time
r
v . (1.11)
t
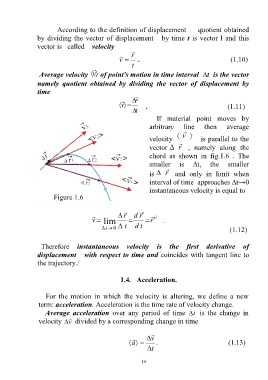
If material point moves by
arbitrary then average
line
v
velocity is parallel to the
vector r , namely along the
chord as shown in fig.1.6 . The
smaller is ∆t, the smaller
is r and only in limit when
interval of time approaches ∆t→0
instantaneous velocity is equal to
Figure 1.6
r d r /
v lim r .
t 0 t t d (1.12)
Therefore instantaneous velocity is the first derivative of
displacement with respect to time and coincides with tangent line to
the trajectory./
1.4. Acceleration.
For the motion in which the velocity is altering, we define a new
term: acceleration. Acceleration is the time rate of velocity change.
Average acceleration over any period of time t is the change in
velocity v divided by a corresponding change in time
v
a . (1.13)
t
14