Page 91 - 6880
P. 91
- 14 days 5.71
The sequence of forecast and assessment of the radiation situation
The forecast and assessment of the radiation situation is carried out in the
following way:
1. Definition of the size of zones of radioactive contamination and the
possibility getting object into an area of contamination.
To do this, determine:
- categories of stability of the atmosphere (degree of vertical air resistance –
DVAR), which determine according to the table 8.2 (if unknown);
- average moving speed of the radioactive cloud V aver. according to the
table 8.4;
- the size of the forecasted zones of radioactive contamination according to
the table 8.5 depending on clouds speed and categories of atmospheric stability,
percentage of thrown radioactive substances, type of reactor;
- will the object be in the contamination zone, in what zone and location in
the zone, based on the distance of the object to the NPP, the zones size and the
direction of the wind – will be at the conditions of R <L; β = β -180°.
0
v
0
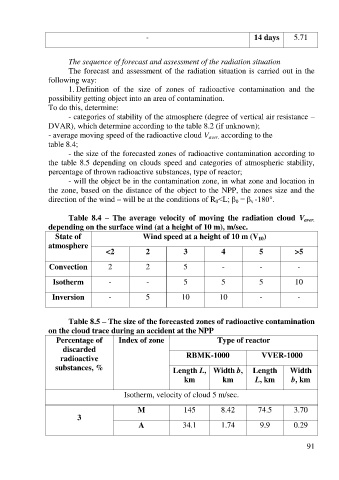
Table 8.4 – The average velocity of moving the radiation cloud V aver.
depending on the surface wind (at a height of 10 m), m/sec.
State of Wind speed at a height of 10 m (V )
10
atmosphere
<2 2 3 4 5 >5
Convection 2 2 5 - - -
Isotherm - - 5 5 5 10
Inversion - 5 10 10 - -
Table 8.5 – The size of the forecasted zones of radioactive contamination
on the cloud trace during an accident at the NPP
Percentage of Index of zone Type of reactor
discarded
radioactive RBMK-1000 VVER-1000
substances, % Length L, Width b, Length Width
km km L, km b, km
Isotherm, velocity of cloud 5 m/sec.
M 145 8.42 74.5 3.70
3
A 34.1 1.74 9.9 0.29
91