Page 76 - 6848
P. 76
Illumination (E) is the ratio of light flux (F) that falls on the surface element to
the surface area of this element (S):
E=F/S.
The unit of illumination measurement is lux (lx).
The level of illumination is measured with a lux meter that converts luminous
energy into an electrical signal, which is then amplified and offers an easy reading on
a calibrated scale of lux.
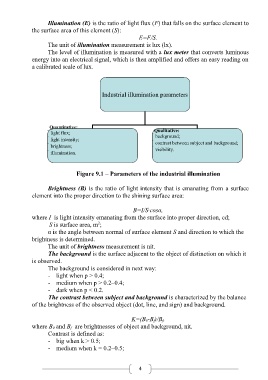
Industrial illumination parameters
Quantitative:
light flux; Qualitative:
background;
light intensity; contrast between subject and background;
brightness;
illumination. visibility.
Figure 9.1 – Parameters of the industrial illumination
Brightness (B) is the ratio of light intensity that is emanating from a surface
element into the proper direction to the shining surface area:
B=I/S·cosα,
where I is light intensity emanating from the surface into proper direction, cd;
2
S is surface area, m ;
α is the angle between normal of surface element S and direction to which the
brightness is determined.
The unit of brightness measurement is nit.
The background is the surface adjacent to the object of distinction on which it
is observed.
The background is considered in next way:
- light when p > 0.4;
- medium when p > 0.2–0.4;
- dark when p < 0.2.
The contrast between subject and background is characterized by the balance
of the brightness of the observed object (dot, line, and sign) and background.
K=(B0-Bf)/Bf,
where B0 and Bf are brightnesses of object and background, nit.
Contrast is defined as:
- big when k > 0.5;
- medium when k = 0.2–0.5;
4