Page 24 - 6200
P. 24
Grammar Section
PASSIVE VOICE
The passive is formed by using the appropriate tense of the verb to be + past participle.
Present Perfect Continuous, Future Continuous, Past Perfect Continuous are not normally used in
the passive.
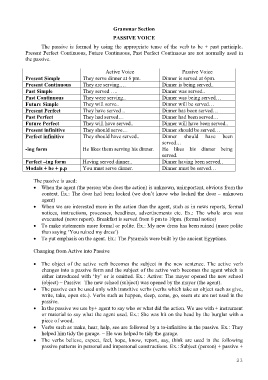
Active Voice Passive Voice
Present Simple They serve dinner at 6 pm. Dinner is served at 6pm.
Present Continuous They are serving…. Dinner is being served..
Past Simple They served …. Dinner was served..
Past Continuous They were serving.. Dinner was being served…
Future Simple They will serve.. Dinner will be served…
Present Perfect They have served .. Dinner has been served…
Past Perfect They had served… Dinner had been served…
Future Perfect They will have served.. Dinner will have been served..
Present infinitive They should serve… Dinner should be served…
Perfect infinitive They should have served.. Dinner should have been
served…
-ing form He likes them serving his dinner. He likes his dinner being
served.
Perfect –ing form Having served dinner.. Dinner having been served..
Modals + be + p.p You must serve dinner. Dinner must be served…
The passive is used:
When the agent (the person who does the action) is unknown, unimportant, obvious from the
context. Ex.: The door had been locked (we don’t know who locked the door – unknown
agent)
When we are interested more in the action than the agent, such as in news reports, formal
notices, instructions, processes, headlines, advertisements etc. Ex.: The whole area was
evacuated (news report). Breakfast is served from 6 pm to 10pm. (formal notice)
To make statements more formal or polite. Ex.: My new dress has been ruined (more polite
than saying ‘You ruined my dress’)
To put emphasis on the agent. Ex.: The Pyramids were built by the ancient Egyptians.
Changing from Active into Passive
The object of the active verb becomes the subject in the new sentence. The active verb
changes into a passive form and the subject of the active verb becomes the agent which is
either introduced with ‘by’ or is omitted. Ex.: Active: The mayor opened the new school
(object) – Passive: The new school (subject) was opened by the mayor (the agent).
The passive can be used only with transitive verbs (verbs which take an object such as give,
write, take, open etc.). Verbs such as happen, sleep, come, go, seem etc are not used in the
passive.
In the passive we use by+ agent to say who or what did the action. We use with + instrument
or material to say what the agent used. Ex.: She was hit on the head by the burglar with a
piece of wood.
Verbs such as make, hear, help, see are followed by a to-infinitive in the passive. Ex.: They
helped him tidy the garage. – He was helped to tidy the garage.
The verbs believe, expect, feel, hope, know, report, say, think are used in the following
passive patterns in personal and impersonal constructions. Ex.: Subject (person) + passive +
23