Page 349 - 4637
P. 349
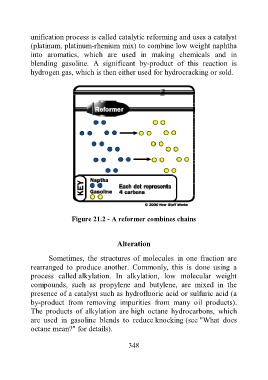
unification process is called catalytic reforming and uses a catalyst
(platinum, platinum-rhenium mix) to combine low weight naphtha
into aromatics, which are used in making chemicals and in
blending gasoline. A significant by-product of this reaction is
hydrogen gas, which is then either used for hydrocracking or sold.
Figure 21.2 - A reformer combines chains
Alteration
Sometimes, the structures of molecules in one fraction are
rearranged to produce another. Commonly, this is done using a
process called alkylation. In alkylation, low molecular weight
compounds, such as propylene and butylene, are mixed in the
presence of a catalyst such as hydrofluoric acid or sulfuric acid (a
by-product from removing impurities from many oil products).
The products of alkylation are high octane hydrocarbons, which
are used in gasoline blends to reduce knocking (see "What does
octane mean?" for details).
348