Page 6 - 4560
P. 6
1 COMBINATION RESISTANCE
1.1 General concepts
Combination resistance occurs when in the cross-sections of
the rod at least two internal power factors simultaneously operate
(the exception is direct cross-ply, which is referred to simply rod
resistance, as in practical calculations the influence of shear force
is usually neglected).
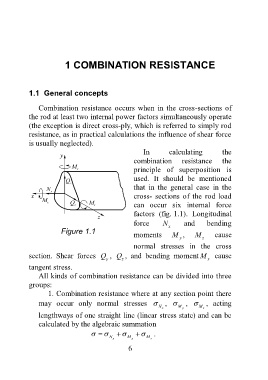
In calculating the
combination resistance the
principle of superposition is
used. It should be mentioned
that in the general case in the
cross- sections of the rod load
can occur six internal force
factors (fig. 1.1). Longitudinal
force N and bending
x
Figure 1.1
moments M , M cause
y z
normal stresses in the cross
section. Shear forces Q , Q , and bending moment M cause
y z x
tangent stress.
All kinds of combination resistance can be divided into three
groups:
1. Combination resistance where at any section point there
may occur only normal stresses , , , acting
N x M y M z
lengthways of one straight line (linear stress state) and can be
calculated by the algebraic summation
.
N M M
x y z
6