Page 14 - 4560
P. 14
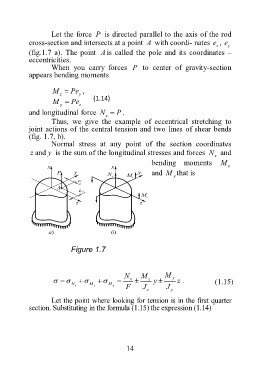
Let the force P is directed parallel to the axis of the rod
cross-section and intersects at a point A with coordi- nates e , e
z y
(fig.1.7 a). The point A is called the pole and its coordinates –
eccentricities.
When you carry forces P to center of gravity-section
appears bending moments
M Pe ,
z y
M Pe (1.14)
y z
and longitudinal force N P .
x
Thus, we give the example of eccentrical stretching to
joint actions of the central tension and two lines of shear bends
(fig. 1.7, b).
Normal stress at any point of the section coordinates
z and y is the sum of the longitudinal stresses and forces N and
x
bending moments M
z
and M that is
y
Figure 1.7
N M M y
x z y z . (1.15)
N M M
x z y F J J
z y
Let the point where looking for tension is in the first quarter
section. Substituting in the formula (1.15) the expression (1.14)
14