Page 67 - Microsoft Word - 4236
P. 67
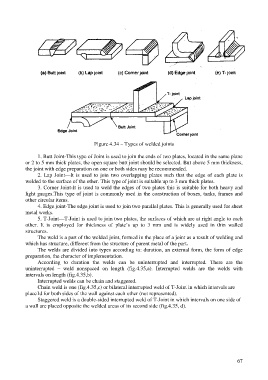
Figure 4.34 – Types of welded joints
1. Butt Joint-This type of Joint is used to join the ends of two plates, located in the same plane
or 2 to 5 mm thick plates, the open square butt joint should be selected. But above 5 mm thickness,
the joint with edge preparation on one or both sides may be recommended.
2. Lap Joint—It is used to join two overlapping plates such that the edge of each plate is
welded to the surface of the other. This type of joint is suitable up to 3 mm thick plates.
3. Corner Joint-It is used to weld the edges of two plates this is suitable for both heavy and
light gauges.This type of joint is commonly used in the construction of boxes, tanks, frames and
other circular items.
4. Edge joint-The edge joint is used to join two parallel plates. This is generally used for sheet
metal works.
5. T-Joint—T-Joint is used to join two plates, the surfaces of which are at right angle to each
other. It is employed for thickness of plate’s up to 3 mm and is widely used in thin walled
structures.
The weld is a part of the welded joint, formed in the place of a joint as a result of welding and
which has structure, different from the structure of parent metal of the part.
The welds are divided into types according to: duration, an external form, the form of edge
preparation, the character of implementation.
According to duration the welds can be uninterrupted and interrupted. There are the
uninterrupted – weld nonspaced on length (fig.4.35,а). Interrupted welds are the welds with
intervals on length (fig.4.35,b).
Interrupted welds can be chain and staggered.
Chain weld is one (fig.4.35,c) or bilateral interrupted weld of T-Joint in which intervals are
place1d for both sides of the wall against each other (not represented).
Staggered weld is a double-sided interrupted weld of T-Joint in which intervals on one side of
a wall are placed opposite the welded areas of its second side (fig.4.35, d).
67