Page 20 - 4234
P. 20
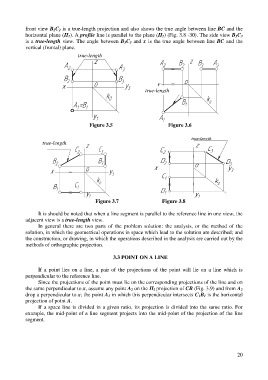
front view B 2C 2 is a true-length projection and also shows the true angle between line BC and the
horizontal plane (Π 1). A profile line is parallel to the plane (Π 2) (Fig. 3.8 -30). The side view B 3C 3
is a true-length view. The angle between B 3C 3 and x is the true angle between line BC and the
vertical (frontal) plane.
true-length
true-length
Figure 3.5 Figure 3.6
true-length
true-length величина
Figure 3.7 Figure 3.8
It is should be noted that when a line segment is parallel to the reference line in one view, the
adjacent view is a true-length view.
In general there are two parts of the problem solution: the analysis, or the method of the
solution, in which the geometrical operations in space which lead to the solution are described; and
the construction, or drawing, in which the operations described in the analysis are carried out by the
methods of orthographic projection.
3.3 POINT ON A LINE
If a point lies on a line, a pair of the projections of the point will lie on a line which is
perpendicular to the reference line.
Since the projections of the point must lie on the corresponding projections of the line and on
the same perpendicular to x, assume any point A 2 on the Π 2 projection of CB (Fig. 3.9) and from A 2
drop a perpendicular to x; the point A 1 in which this perpendicular intersects C 1B 1 is the horizontal
projection of point A.
If a space line is divided in a given ratio, its projection is divided into the same ratio. For
example, the mid-point of a line segment projects into the mid-point of the projection of the line
segment.
20