Page 104 - 4167
P. 104
of the element . When the length is considerably longer than the width
and the thickness, the element is called a beam. The beam experiencing
bending is shown in fig.8.4,where h is sagging deflection
3
1 l 3
h F (8.10)
E a 4 b 3
8.5Torsion deformation
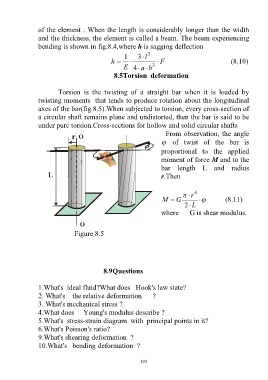
Torsion is the twisting of a straight bar when it is loaded by
twisting moments that tends to produce rotation about the longitudinal
axes of the bar(fig.8.5).When subjected to torsion, every cross-section of
a circular shaft remains plane and undistorted, then the bar is said to be
under pure torsion.Cross-sections for hollow and solid circular shafts
From observation, the angle
of twist of the bar is
proportional to the applied
moment of force M and to the
bar length L and radius
r.Then
r 4
M G (8.11)
2 L
where G is shear modulus.
Figure 8.5
8.9Questions
1.What's ideal fluid?What does Hook's law state?
2. What's the relative deformation ?
3. What's mechanical stress ?
4.What does Young's modulus describe ?
5.What's stress-strain diagram with principal points in it?
6.What's Poisson's ratio?
9.What's shearing deformation ?
10.What's bending deformation ?
103