Page 103 - 4167
P. 103
DenisPoisson (1781–1840) french mathematician, geometer, and
physicist) and is denoted by
y
z (8.7)
x y
For most steel Poisson's ratio lies in the range of 0.25 to 0.3.
8.3 Shearing deformation
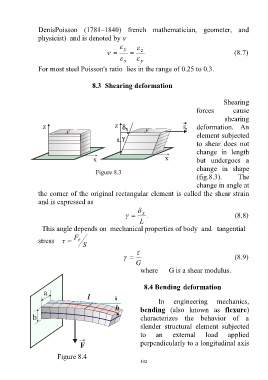
Shearing
forces cause
shearing
deformation. An
element subjected
to shear does not
change in length
but undergoes a
change in shape
Figure 8.3
(fig.8.3). The
change in angle at
the corner of the original rectangular element is called the shear strain
and is expressed as
x
. (8.8)
L
This angle depends on mechanical properties of body and tangential
F
stress
S
(8.9)
G
where G is a shear modulus.
8.4 Bending deformation
In engineering mechanics,
bending (also known as flexure)
characterizes the behavior of a
slender structural element subjected
to an external load applied
perpendicularly to a longitudinal axis
Figure 8.4
102