Page 83 - 6880
P. 83
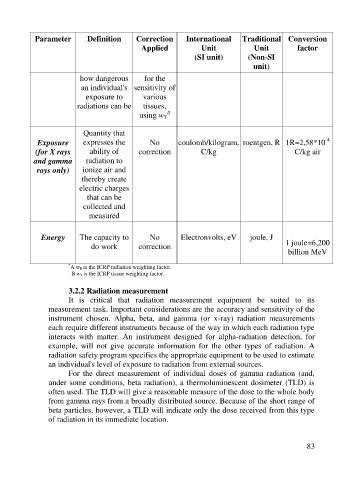
Parameter Definition Correction International Traditional Conversion
Applied Unit Unit factor
(SI unit) (Non-SI
unit)
how dangerous for the
an individual's sensitivity of
exposure to various
radiations can be tissues,
B
using w
T
Quantity that
-4
Exposure expresses the No coulomb/kilogram, roentgen, R 1R=2,58*10
(for X rays ability of correction C/kg C/kg air
and gamma radiation to
rays only) ionize air and
thereby create
electric charges
that can be
collected and
measured
Energy The capacity to No Electronvolts, eV joule, J
do work correction 1 joule=6,200
billion MeV
*
A w R is the ICRP radiation weighting factor.
B w T is the ICRP tissue weighting factor.
3.2.2 Radiation measurement
It is critical that radiation measurement equipment be suited to its
measurement task. Important considerations are the accuracy and sensitivity of the
instrument chosen. Alpha, beta, and gamma (or x-ray) radiation measurements
each require different instruments because of the way in which each radiation type
interacts with matter. An instrument designed for alpha-radiation detection, for
example, will not give accurate information for the other types of radiation. A
radiation safety program specifies the appropriate equipment to be used to estimate
an individual's level of exposure to radiation from external sources.
For the direct measurement of individual doses of gamma radiation (and,
under some conditions, beta radiation), a thermoluminescent dosimeter (TLD) is
often used. The TLD will give a reasonable measure of the dose to the whole body
from gamma rays from a broadly distributed source. Because of the short range of
beta particles, however, a TLD will indicate only the dose received from this type
of radiation in its immediate location.
83