Page 69 - 6880
P. 69
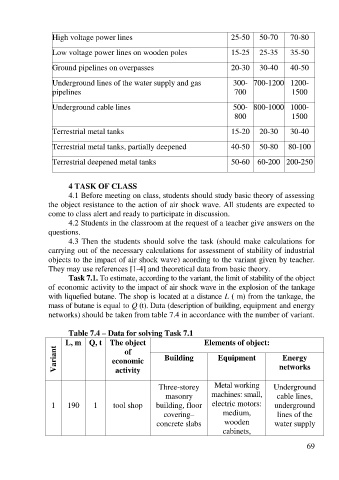
High voltage power lines 25-50 50-70 70-80
Low voltage power lines on wooden poles 15-25 25-35 35-50
Ground pipelines on overpasses 20-30 30-40 40-50
Underground lines of the water supply and gas 300- 700-1200 1200-
pipelines 700 1500
Underground cable lines 500- 800-1000 1000-
800 1500
Terrestrial metal tanks 15-20 20-30 30-40
Terrestrial metal tanks, partially deepened 40-50 50-80 80-100
Terrestrial deepened metal tanks 50-60 60-200 200-250
4 TASK OF CLASS
4.1 Before meeting on class, students should study basic theory of assessing
the object resistance to the action of air shock wave. All students are expected to
come to class alert and ready to participate in discussion.
4.2 Students in the classroom at the request of a teacher give answers on the
questions.
4.3 Then the students should solve the task (should make calculations for
carrying out of the necessary calculations for assessment of stability of industrial
objects to the impact of air shock wave) acording to the variant given by teacher.
They may use references [1-4] and theoretical data from basic theory.
Task 7.1. To estimate, according to the variant, the limit of stability of the object
of economic activity to the impact of air shock wave in the explosion of the tankage
with liquefied butane. The shop is located at a distance L ( m) from the tankage, the
mass of butane is equal to Q (t). Data (description of building, equipment and energy
networks) should be taken from table 7.4 in accordance with the number of variant.
Table 7.4 – Data for solving Task 7.1
L, m Q, t The object Elements of object:
Variant economic Building Equipment networks
of
Energy
activity
Three-storey Metal working Underground
masonry machines: small, cable lines,
1 190 1 tool shop building, floor electric motors: underground
covering– medium, lines of the
concrete slabs wooden water supply
cabinets,
69