Page 53 - 6880
P. 53
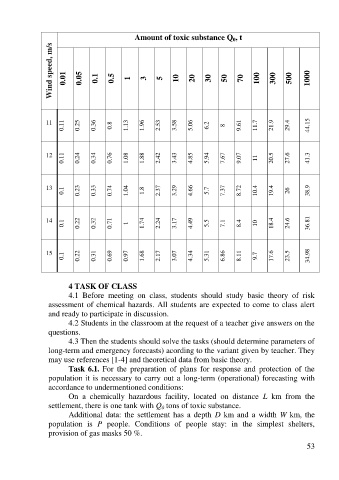
Amount of toxic substance Q , t
0
Wind speed, m/s 0.01 0.05 0.1 0.5 1 3 5 10 20 30 50 70 100 300 500 1000
0.11 0.25 0.36 0.8 1.13 1.96 2.53 3.58 5.06 6.2 8 9.61 11.7 21.9 29.4 44.15
11
0.11 0.24 0.34 0.76 1.08 1.88 2.42 3.43 4.85 5.94 7.67 9.07 11 20.5 27.6 41.3
12
13 0.1 0.23 0.33 0.74 1.04 1.8 2.37 3.29 4.66 5.7 7.37 8.72 10.4 19.4 26 38.9
14
0.1 0.22 0.32 0.71 1 1.74 2.24 3.17 4.49 5.5 7.1 8.4 10 18.4 24.6 36.81
15
0.1 0.22 0.31 0.69 0.97 1.68 2.17 3.07 4.34 5.31 6.86 8.11 9.7 17.6 23.5 34.98
4 TASK OF CLASS
4.1 Before meeting on class, students should study basic theory of risk
assessment of chemical hazards. All students are expected to come to class alert
and ready to participate in discussion.
4.2 Students in the classroom at the request of a teacher give answers on the
questions.
4.3 Then the students should solve the tasks (should determine parameters of
long-term and emergency forecasts) acording to the variant given by teacher. They
may use references [1-4] and theoretical data from basic theory.
Task 6.1. For the preparation of plans for response and protection of the
population it is necessary to carry out a long-term (operational) forecasting with
accordance to undermentioned conditions:
On a chemically hazardous facility, located on distance L km from the
settlement, there is one tank with Q tons of toxic substance.
0
Additional data: the settlement has a depth D km and a width W km, the
population is P people. Conditions of people stay: in the simplest shelters,
provision of gas masks 50 %.
53