Page 51 - 6848
P. 51
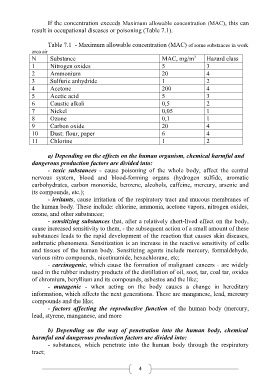
If the concentration exceeds Maximum allowable concentration (MAC), this can
result in occupational diseases or poisoning (Table 7.1).
Table 7.1 - Maximum allowable concentration (MAC) of some substances in work
area air
N Substance MAC, mg/m 3 Hazard class
1 Nitrogen oxides 5 3
2 Ammonium 20 4
3 Sulfuric anhydride 1 2
4 Acetone 200 4
5 Acetic acid 5 3
6 Caustic alkali 0,5 2
7 Nickel 0,05 1
8 Ozone 0,1 1
9 Carbon oxide 20 4
10 Dust: flour, paper 6 4
11 Chlorine 1 2
a) Depending on the effects on the human organism, chemical harmful and
dangerous production factors are divided into:
- toxic substances - cause poisoning of the whole body, affect the central
nervous system, blood and blood-forming organs (hydrogen sulfide, aromatic
carbohydrates, carbon monoxide, benzene, alcohols, caffeine, mercury, arsenic and
its compounds, etc.);
- irritants, cause irritation of the respiratory tract and mucous membranes of
the human body. These include: chlorine, ammonia, acetone vapors, nitrogen oxides,
ozone, and other substances;
- sensitizing substances that, after a relatively short-lived effect on the body,
cause increased sensitivity to them, - the subsequent action of a small amount of these
substances leads to the rapid development of the reaction that causes skin diseases,
asthmatic phenomena. Sensitization is an increase in the reactive sensitivity of cells
and tissues of the human body. Sensitizing agents include mercury, formaldehyde,
various nitro compounds, nicotinamide, hexachlorane, etc;
- carcinogenic, which cause the formation of malignant cancers - are widely
used in the rubber industry products of the distillation of oil, soot, tar, coal tar, oxides
of chromium, beryllium and its compounds, asbestos and the like;
- mutagenic - when acting on the body causes a change in hereditary
information, which affects the next generations. These are manganese, lead, mercury
compounds and the like;
- factors affecting the reproductive function of the human body (mercury,
lead, styrene, manganese, and more
b) Depending on the way of penetration into the human body, chemical
harmful and dangerous production factors are divided into:
- substances, which penetrate into the human body through the respiratory
tract;
4