Page 32 - 6727
P. 32
Economic Theory
P – profit includes the profits made by both individuals and
corporations;
SA – statistical adjustments (corporate income taxes).
The expenditure approach measures GDP as the sum of consumption
expenditure, investment, government purchases of goods and services, and
net exports:
GDPcost = C + I + G + NX, (3.2)
C – consumption is spending by households on goods and services;
I – investment is the purchase of capital equipment, inventories, and
structures;
G – government purchases include spending on goods and services by
local, state, and federal governments. But it does not include transfer
payments like social security benefits. Transfer payments are not included
because they do not represent income from current production;
NX – net exports equal the purchases of domestically produced goods
by foreigners (exports) minus the domestic purchases of foreign goods
(imports).
Net exports are positive when the value of our exports is greater than
the value of our imports and negative when the value of our imports is
greater than the value of our exports. Net exports represent the net
expenditure from abroad on our goods and services, which provides
income for domestic producers.
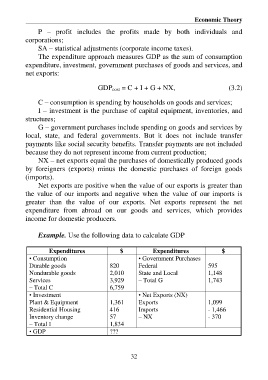
Example. Use the following data to calculate GDP
Expenditures $ Expenditures $
• Consumption • Government Purchases
Durable goods 820 Federal 595
Nondurable goods 2,010 State and Local 1,148
Services 3,929 – Total G 1,743
– Total C 6,759
• Investment • Net Exports (NX)
Plant & Equipment 1,361 Exports 1,099
Residential Housing 416 Imports - 1,466
Inventory change 57 – NX - 370
– Total I 1,834
• GDP ???
32