Page 106 - 6727
P. 106
Economic Theory
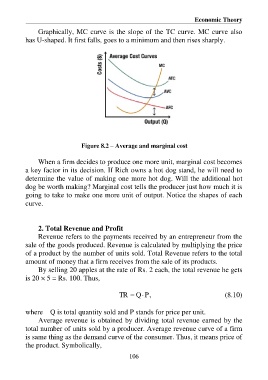
Graphically, MC curve is the slope of the TC curve. MC curve also
has U-shaped. It first falls, goes to a minimum and then rises sharply.
Figure 8.2 – Average and marginal cost
When a firm decides to produce one more unit, marginal cost becomes
a key factor in its decision. If Rich owns a hot dog stand, he will need to
determine the value of making one more hot dog. Will the additional hot
dog be worth making? Marginal cost tells the producer just how much it is
going to take to make one more unit of output. Notice the shapes of each
curve.
2. Total Revenue and Profit
Revenue refers to the payments received by an entrepreneur from the
sale of the goods produced. Revenue is calculated by multiplying the price
of a product by the number of units sold. Total Revenue refers to the total
amount of money that a firm receives from the sale of its products.
By selling 20 apples at the rate of Rs. 2 each, the total revenue he gets
is 20 × 5 = Rs. 100. Thus,
TR Q P , (8.10)
where Q is total quantity sold and P stands for price per unit.
Average revenue is obtained by dividing total revenue earned by the
total number of units sold by a producer. Average revenue curve of a firm
is same thing as the demand curve of the consumer. Thus, it means price of
the product. Symbolically,
106