Page 29 - 6653
P. 29
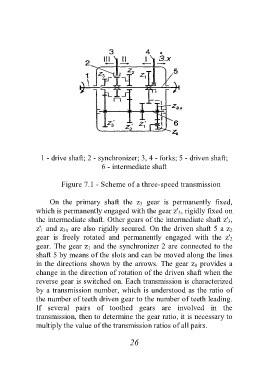
1 - drive shaft; 2 - synchronizer; 3, 4 - forks; 5 - driven shaft;
6 - intermediate shaft
Figure 7.1 - Scheme of a three-speed transmission
On the primary shaft the z 3 gear is permanently fixed,
which is permanently engaged with the gear z' 3, rigidly fixed on
the intermediate shaft. Other gears of the intermediate shaft z' 3,
z' 1 and z 3x are also rigidly secured. On the driven shaft 5 a z 2
gear is freely rotated and permanently engaged with the z' 2
gear. The gear z 1 and the synchronizer 2 are connected to the
shaft 5 by means of the slots and can be moved along the lines
in the directions shown by the arrows. The gear z 0 provides a
change in the direction of rotation of the driven shaft when the
reverse gear is switched on. Each transmission is characterized
by a transmission number, which is understood as the ratio of
the number of teeth driven gear to the number of teeth leading.
If several pairs of toothed gears are involved in the
transmission, then to determine the gear ratio, it is necessary to
multiply the value of the transmission ratios of all pairs.
26