Page 77 - 6641
P. 77
(concentrated), sodium hydroxide, chloride acid
(concentrated), sulfuric acid (concentrated), 10% solution
sodium nitrite, nitric acid (concentrated), test tubes, glass
rods.
The theoretical part
Amines are derivatives of ammonia, the molecule of
which one or more Hydrogen atoms replaced by
hydrocarbon radicals.
Depending on the number of substituted Hydrogen
atoms there are primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Aliphatic amines are relatively strong bases, and therefore
with acids they form salts. Primary amines react with
halogenoalkanes forming secondary, secondary – tertiary
amines. Replacement of Hydrogen atoms on alcini radical is
the reaction alcelaphine. The interaction of primary or
secondary amines with carboxylic acids halogenoalkane that
leads to the replacement of Hydrogen atoms of the amino
group in the acid residue, which is called acyl, the acylation
is a reaction.
Primary aliphatic amines react with nutritiou acid,
forming alcohols, secondary – ntropali, tertiary and does not
react. This reaction is used to detect amines. Aromatic
amines are derivatives of ammonia in which the Hydrogen
atoms (one, two, or all three) substituted on the aromatic
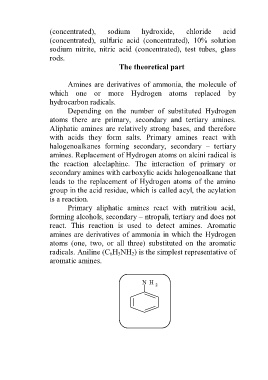
radicals. Aniline (C 6H 5NH 2) is the simplest representative of
aromatic amines.
N H 2