Page 158 - 6484
P. 158
Control
Proactivity Behavioral control Outcome control
Feedforw Organizational culture Market demand or
ard control economic forecasts
Concurre Hands-on management The real-time speed of a
nt control supervision during a project production line
Feedback Qualitative measures of Financial measures such
control customer satisfaction as profitability, sales growth
Concurrent Controls
The process of monitoring and adjusting ongoing activities and processes is
known as concurrent control. Such controls are not necessarily proactive, but they
can prevent problems from becoming worse. For this reason, we often describe
concurrent control as real-time control because it deals with the present. An example
of concurrent control might be adjusting the water temperature of the water while
taking a shower.
Feedback Controls
Finally, feedback controls involve gathering information about a completed
activity, evaluating that information, and taking steps to improve the similar activities
in the future. This is the least proactive of controls and is generally a basis for
reactions. Feedback controls permit managers to use information on past performance
to bring future performance in line with planned objectives.
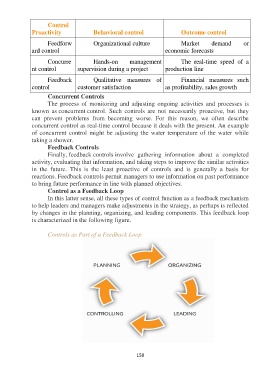
Control as a Feedback Loop
In this latter sense, all these types of control function as a feedback mechanism
to help leaders and managers make adjustments in the strategy, as perhaps is reflected
by changes in the planning, organizing, and leading components. This feedback loop
is characterized in the following figure.
Controls as Part of a Feedback Loop
158