Page 11 - 6413
P. 11
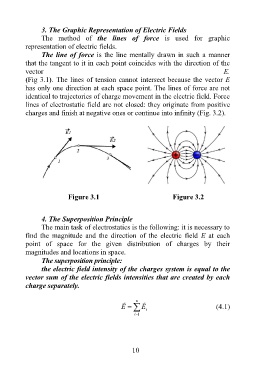
3. The Graphic Representation of Electric Fields
The method of the lines of force is used for graphic
representation of electric fields.
The line of force is the line mentally drawn in such a manner
that the tangent to it in each point coincides with the direction of the
vector E.
(Fig 3.1). The lines of tension cannot intersect because the vector E
has only one direction at each space point. The lines of force are not
identical to trajectories of charge movement in the electric field. Force
lines of electrostatic field are not closed: they originate from positive
charges and finish at negative ones or continue into infinity (Fig. 3.2).
Figure 3.1 Figure 3.2
4. The Superposition Principle
The main task of electrostatics is the following: it is necessary to
find the magnitude and the direction of the electric field E at each
point of space for the given distribution of charges by their
magnitudes and locations in space.
The superposition principle:
the electric field intensity of the charges system is equal to the
vector sum of the electric fields intensities that are created by each
charge separately.
n
E E (4.1)
i
i 1
10