Page 53 - 6273
P. 53
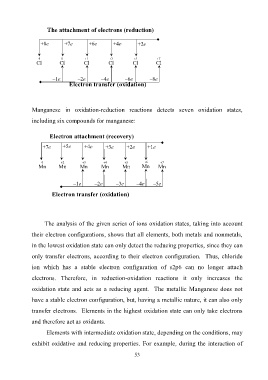
The attachment of electrons (reduction)
+8e +7e +6e +4e +2e
-1 0 1 3 5 7
Сl Сl Сl Сl Сl Сl
–1e –2e –4e –6e –8e
Electron transfer (oxidation)
Manganese in oxidation-reduction reactions detects seven oxidation states,
including six compounds for manganese:
Electron attachment (recovery)
+7e +5e +4e +3e +2e +1e
0 2 3 4 5 6 7
Mn Mn Mn Mn Mn Mn Mn
–1e –2e –3e –4e –5e
Electron transfer (oxidation)
The analysis of the given series of ions oxidation states, taking into account
their electron configurations, shows that all elements, both metals and nonmetals,
in the lowest oxidation state can only detect the reducing properties, since they can
only transfer electrons, according to their electron configuration. Thus, chloride
ion which has a stable electron configuration of s2p6 can no longer attach
electrons. Therefore, in reduction-oxidation reactions it only increases the
oxidation state and acts as a reducing agent. The metallic Manganese does not
have a stable electron configuration, but, having a metallic nature, it can also only
transfer electrons. Elements in the highest oxidation state can only take electrons
and therefore act as oxidants.
Elements with intermediate oxidation state, depending on the conditions, may
exhibit oxidative and reducing properties. For example, during the interaction of
53