Page 88 - 6099
P. 88
λ = 0. The general solution is
ψ = ax + b.
0
ψ (0) = 0 ⇒ a = 0.
0
ψ(1) + ψ (1) = 0 ⇒ b + 0 = 0.
Thus λ = 0 is not an eigenvalue.
λ > 0. The general solution is
√ √
ψ = a cos( λx) + b sin( λx).
0
ψ (0) ⇒ b = 0.
√ √ √
0
ψ(1) + ψ (1) = 0 ⇒ a cos( λ) − a λ sin( λ) = 0
√ √ √
⇒ cos( λ) = λ sin( λ)
√ √
⇒ λ = cot( λ)
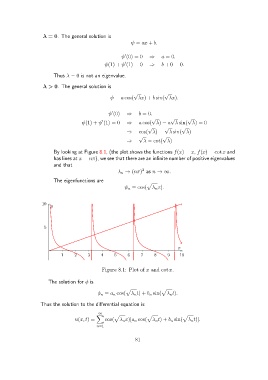
By looking at Figure 8.1, (the plot shows the functions f(x) = x, f(x) = cot x and
has lines at x = nπ), we see that there are an infinite number of positive eigenvalues
and that
2
λ n → (nπ) as n → ∞.
The eigenfunctions are
p
ψ n = cos( λ n x).
10
y
5
x
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Figure 8.1: Plot of x and cot x.
The solution for φ is
p p
φ n = a n cos( λ n t) + b n sin( λ n t).
Thus the solution to the differential equation is
∞
X p p p
u(x, t) = cos( λ n x)[a n cos( λ n t) + b n sin( λ n t)].
n=1
81