Page 31 - 6099
P. 31
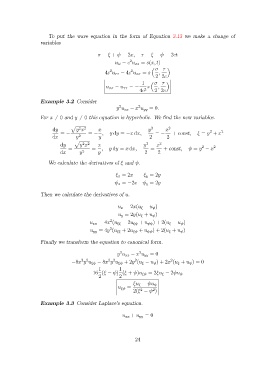
To put the wave equation in the form of Equation 3.13 we make a change of
variables
σ = ξ + ψ = 2x, τ = ξ − ψ = 2ct
2
u tt − c u xx = s(x, t)
σ τ
2
2
4c u ττ − 4c u σσ = s ,
2 2c
1 σ τ
u σσ − u ττ = − s ,
4c 2 2 2c
Example 3.2 Consider
2
2
y u xx − x u yy = 0.
For x 6= 0 and y 6= 0 this equation is hyperbolic. We find the new variables.
p
2 2
dy y x x y 2 x 2 2 2
= − = − , y dy = −x dx, = − + const, ξ = y + x
dx y 2 y 2 2
p
2 2
dy y x x y 2 x 2
2
= = , y dy = x dx, = + const, ψ = y − x 2
dx y 2 y 2 2
We calculate the derivatives of ξ and ψ.
ξ x = 2x ξ y = 2y
ψ x = −2x ψ y = 2y
Then we calculate the derivatives of u.
u x = 2x(u ξ − u ψ )
u y = 2y(u ξ + u ψ )
2
u xx = 4x (u ξξ − 2u ξψ + u ψψ ) + 2(u ξ − u ψ )
2
u yy = 4y (u ξξ + 2u ξψ + u ψψ ) + 2(u ξ + u ψ )
Finally we transform the equation to canonical form.
2
2
y u xx − x u yy = 0
2 2
2
2 2
2
−8x y u ξψ − 8x y u ξψ + 2y (u ξ − u ψ ) + 2x (u ξ + u ψ ) = 0
1 1
16 (ξ − ψ) (ξ + ψ)u ξψ = 2ξu ξ − 2ψu ψ
2 2
ξu ξ − ψu ψ
u ξψ =
2
2
2(ξ − ψ )
Example 3.3 Consider Laplace’s equation.
u xx + u yy = 0
24